In this blog, I will discuss Puppet architecture at the very basic level in a very simple way.
Consider a system administrator working with multiple servers. If one of the servers has an issue, they can easily fix it. The situation becomes problematic, however, when multiple servers are down.
This is where Puppet can help.
With Puppet, you can write simple code and deploy it to the servers that have issues. After the code runs, all servers are rolled back to their previous working states or set to the new desired states in a matter of seconds. Puppet can also be used to deploy software and add security, all through simple codes.
What is Puppet?
Puppet is a configuration management tool ensuring that all systems are configured to a desired and predictable state.
Puppet is an open-source DevOps system management tool. It is used to centralize and automate the configuration management procedure. This tool is developed using Ruby DSL (domain-specific language). Puppet tool deploys, configures, and manages the servers.
Architecture
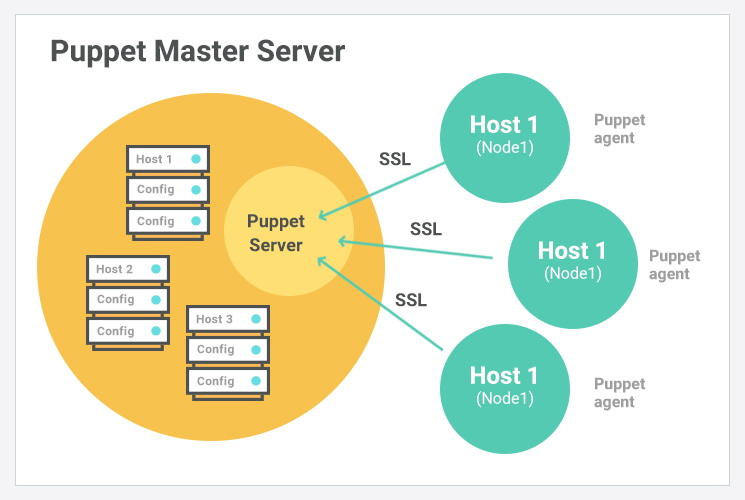
Puppet Master
Puppet Master is the key mechanism which handles all the configuration related stuff. It is a Linux based system in which puppet master software is installed. The puppet master must be in Linux. It applies the configuration to nodes using the Puppet agent.
This is the place where SSL certificates are checked and marked.
Puppet Agent
Puppet Agents are the actual working machines which are installed on client machine and maintained and managed by the Puppet master. They have the Puppet agent daemon service running inside them.
The agent machine can be configured on any operating system such as Windows, Linux, Solaris, or Mac OS.
Config Repository
This is the repo where all nodes and server-related configurations are saved and we can pull these configurations as per requirements.
Facts
Facts are the details related to the node or the master machine, which are basically used for analyzing the current status of any node.It represents a puppet client states such as operating system, network interface, IP address, uptime, and whether the client machine is virtual or not. On the basis of facts, changes are done on any target machine. There are pre-defined and custom facts in Puppet.
Catalog
All the manifest files or configuration which are written in Puppet are first converted to a compiled format called catalog and later those catalogs are applied on the target machine.
Working
- First of all, an agent node sends facts to the master or server and requests for a catalog.
- The master or server compiles and returns the catalog of a node with the help of some information accessed by the master.
- Then the agent applies the catalog to the node by checking every resource mentioned in the catalog. If it identifies resources that are not in their desired state, then makes the necessary adjustments to fix them. Or, it determines in no-op mode, the adjustments would be required to reconcile the catalog.
- And finally, the agent sends a report back to the master.
Components

The Puppet environment can be broken down into the main server environment (shown above) and the client environment. In the main server environment, there is a Puppet master store which stores all configuration files.
Manifests are the actual codes for configuring the clients.
Templates combine code and data to render a final document.
Files are the static content that can be downloaded by the clients.
Modules are a collection of manifests, templates, and files.
Certificate authority allows the master to sign the certificates sent by the client.
The Puppet client is the machine that needs to be configured, consisting of Agent and Facter. The agent continuously interacts with the master server to ensure that the certificates are being updated appropriately. The facter collects the current state of the client that is used and communicates it back through the agent.
That’s it for now but in next blog I will implement Puppet on Azure.

[…] how to create a virtual on Azure using command line. And then If Puppet is new for you, read my this blog […]
LikeLike